In the bustling bazaar of the internet, where information flows like the aromatic scent of saffron in a Tehran market, lies the intricate system of DNS – the Domain Name System. It is the unseen merchant, guiding us seamlessly from familiar names to the numerical addresses that computers understand. Join me, dear reader, as we embark on a journey to demystify how DNS name resolution works, weaving in tales of technology, tradition, and transformation.
The Essence of DNS
Imagine the internet as a sprawling city, vibrant and alive, with countless destinations. In this city, every home or business has an address, much like the IP addresses computers use to communicate. However, for us, remembering these numerical addresses is akin to memorizing the endless rows of shops in Tehran’s Grand Bazaar. This is where DNS steps in, serving as the city’s directory, translating human-friendly domain names into IP addresses.
The Journey of a DNS Query
Step 1: The Initial Request
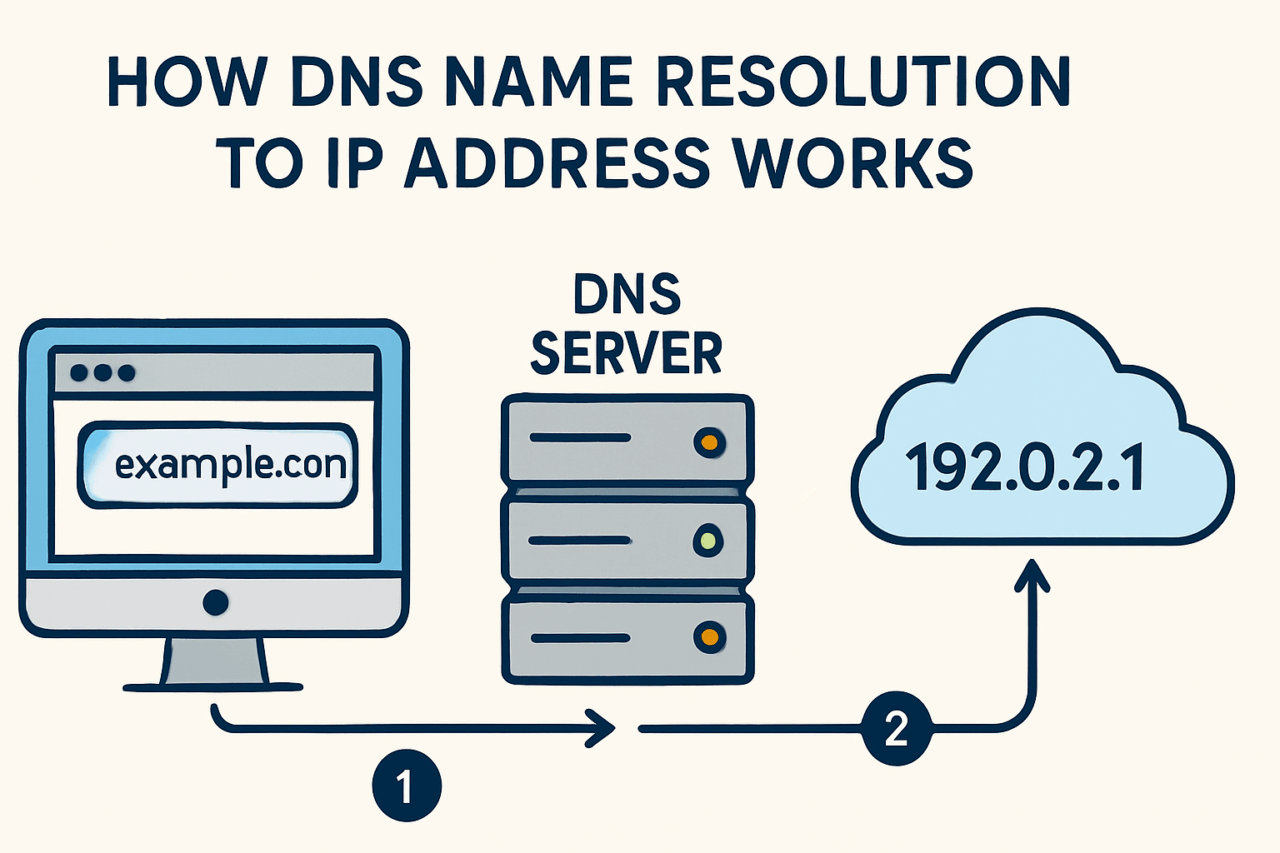
Picture yourself in a traditional Persian tea house, savoring a warm cup of chai. You decide to visit a friend’s new shop. To find it, you ask the shopkeeper, who represents your device’s DNS resolver. This is the first step in DNS name resolution – your browser sends a query to the DNS resolver, asking for the IP address of, say, “example.com”.
Step 2: Consulting the Hierarchy
Much like consulting the elders in a village to trace family lineages, the DNS resolver consults a hierarchy of servers. These hierarchical steps form the backbone of DNS:
-
Root Name Servers: At the pinnacle, these servers hold the key to all top-level domains (TLDs). They direct the resolver to the appropriate TLD server based on the domain’s suffix, such as
.comor.net. -
TLD Name Servers: These servers manage the various domains within their top-level domain. For “example.com”, the TLD server points the resolver toward the authoritative name server responsible for “example.com”.
-
Authoritative Name Servers: The final stop, these servers hold the DNS records for the specific domain. They provide the resolver with the required IP address, completing the journey.
The Art of Caching
In the spirit of efficiency, akin to a Persian carpet weaver who memorizes intricate patterns, DNS resolvers cache responses. This means that for subsequent requests, they can provide answers swiftly, weaving a faster and more responsive internet experience.
A Glimpse into DNS Records
To truly appreciate the elegance of DNS, let’s delve into DNS records. Think of these as the spices in a Persian dish, each contributing a unique flavor to the resolution process.
- A Record: Maps a domain to an IPv4 address.
- AAAA Record: Maps a domain to an IPv6 address.
- CNAME Record: Allows one domain to be an alias for another.
- MX Record: Directs email traffic to the correct mail server.
Here’s a simple DNS record configuration:
example.com. 3600 IN A 192.0.2.1
3600 IN AAAA 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
3600 IN MX 10 mail.example.com.
Security and DNS
In a world where information is as precious as Persian silk, safeguarding DNS queries is crucial. This is where DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) steps in, providing authenticity and integrity, much like the ancient seals of Persian kings.
Conclusion: A Symphony of Technology and Tradition
The dance of DNS name resolution, from names to numbers, is a testament to human ingenuity, akin to the intricate designs of Persian architecture. It is a symphony, harmonizing the demands of technology with the elegance of tradition. As we navigate the vast city of the internet, let us take a moment to appreciate the unseen hands of DNS, guiding us with precision and grace.
In the spirit of learning and discovery, may this tale inspire you to delve deeper into the mysteries of technology, much like the endless tales of Scheherazade, each filled with wonder and wisdom.
Comments (0)
There are no comments here yet, you can be the first!